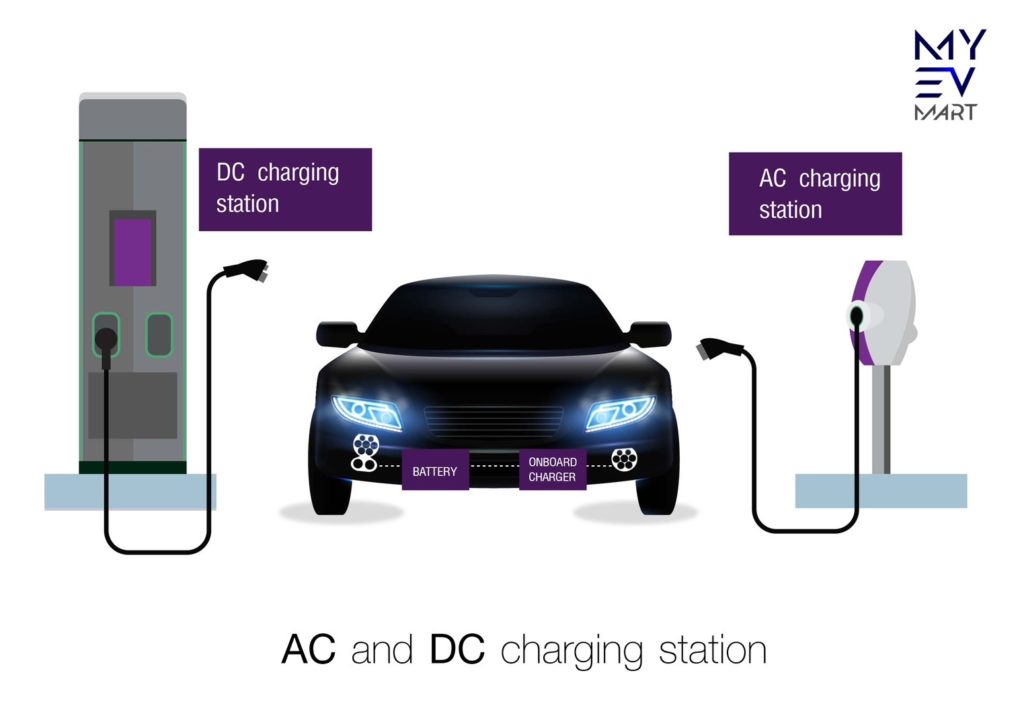
There are two types of electricity charging options that can be used for charging electric vehicles. They are known as Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) power EV charging source.
The power coming from the electricity grid is always Alternating Current (AC). However, an electric car battery is only able to accept Direct Current (DC). The main difference between AC and DC charging is the location where the AC power gets converted. It can be converted outside or inside the car.
At MyEV Mart, we understand how mysterious the world of electric vehicles can be, especially regarding charging. That is why we have created a comprehensive guide to assist you in understanding the various types of EV charging. AC charging, also known as Level 2 charging, is a standard mode of EV charging. AC charging EV is ideal for people with a dedicated charging station at home or work. It is a faster option than Level 1 charging, which uses a standard household outlet.
Depending on the vehicle and charging station capacity, an EV AC charger can provide up to 80 miles of range per hour. Furthermore, some public charging stations provide AC charging EV, making them convenient for on-the-go drivers. Electric vehicle owners must understand the various types of EV charging, including AC charger. MyEV Mart provides a diverse range of EV charging solutions, specializing in smart fast AC chargers, to meet your specific requirements.
The DC charger are usually bigger since the converter is located inside the charging station. It also means that it is faster than the AC chargers when it comes to charging the EV battery.
For AC charging, the converting process happens inside of the car. Electric vehicles have a built-in AC-DC converter called an “onboard charger – OBC” that converts AC to DC power. After converting the power, the car’s battery is charged up.
One significant distinction between AC and DC charging is the price .AC chargers are much cheaper to use and install than DC type. DC chargers are more expensive as installation and grid connection costs are higher.
When your EV car is charged at a DC power point, you can save a lot of time. In most cases, you will have to pay a higher price for the increased charging speed. Meanwhile, charging with AC EV charger is cheaper but takes longer.
If you can charge your EV close to the office or at home, there’s no need to overpay for super-fast charging.
When it comes to price, home charging is the cheaper option and a solution that will definitely be easier on your wallet.
To note other factors that can affect charging speeds include:
- Battery percentage (state of charge remaining)
- State and health of the EV’s battery
- Weather and driving conditions